The march of COVID-19 seems unstoppable as it has made its presence felt in nearly 180 countries. With no prospects of a cure or vaccine being commercially available in the foreseeable future, protecting one self is of utmost importance. While sanitary measures and social distancing can reduce the risk of infection, strengthening your immune system is an equally vital measure.
In the absence of any fixed treatment to fight the coronavirus, boosting the body's immune system can make the fight against the disease a winnable one. Here are a few ways in which you can bolster your body's immune system to fight the virus.
Dealing with existing health conditions
Several studies related to the effect of COVID-19 have suggested that pre-existing medical conditions such as lung disease, hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease put individuals at a larger risk of contracting the disease. Many older adults struggle with these ailments and are at a much larger risk of being infected. Therefore, it is important to keep these illnesses under check.
Also, getting one self vaccinated against the flu may not be a bad idea. As the flu also affects the respiratory system, flu-weakened lungs may be at danger of bearing a bigger brunt of the disease. Keeping the flu away can keep the lungs healthier and help fight the coronavirus in the case of an infection. Additionally, it will reduce the burden on already taxed doctors to focus on COVID-19 patients and not worry about new flu cases.
Pointing towards the last benefit, Dr. Albert Ko, a professor and department chair at the Yale School of Public Health, told Live Science: "I do think immunizing people against influenza has a very important indirect effect."
Eat right to win the fight
"A huge proportion of your immune system is actually in your GI tract," said Dan Peterson, assistant professor of pathology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, while talking about a study on the role of gut health on immunity. Certain cells line the gut walls and produce antibodies that can help fight infections. Hence, a healthy gut can enable the body to put up a stronger resistance by boosting the immune system.
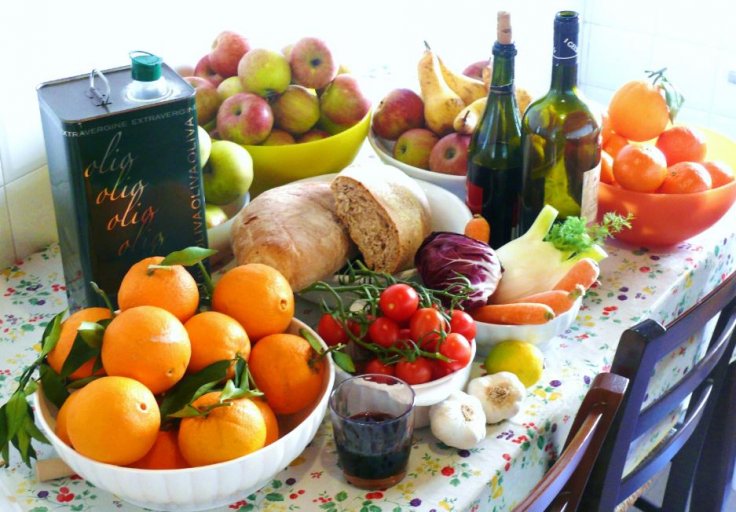

So what can one eat to achieve this? An ideal option is a Mediterranean diet which comprises of fresh vegetables and fruits, nuts, fatty fish, olive oil and whole grains. The design of the diet provides the body with substantial amounts of vital vitamins such as A, B2, B6 and B12, C, D, and E. The diet also provides essential minerals such as iron, selenium, and zinc, along with plant-based antioxidants. Fermented foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut, and kefir will help in promoting good bacteria in the gut.
Studies have also suggested that among older adults who followed a Mediterranean-style diet with adequate physician-prescribed doses of vitamin D supplements, increased levels of T cells —a form of lymphocytes — was noticed after a year; a sign of improved immunity. Processed and fried foods, especially met, can cause more harm than good. So saying good-bye to them is a good idea.
Keep stress at bay
Studies have proven that stress leaves the body susceptible to infections and affects recovery. Stress has also been associated with increased production of cytokines that trigger an inflammatory response. Good habits such as consuming healthy food and sufficient sleep go outside the window due to stress, thereby diminishing the body's immunity. Therefore, dealing with stress plays an important role in boosting immunity.
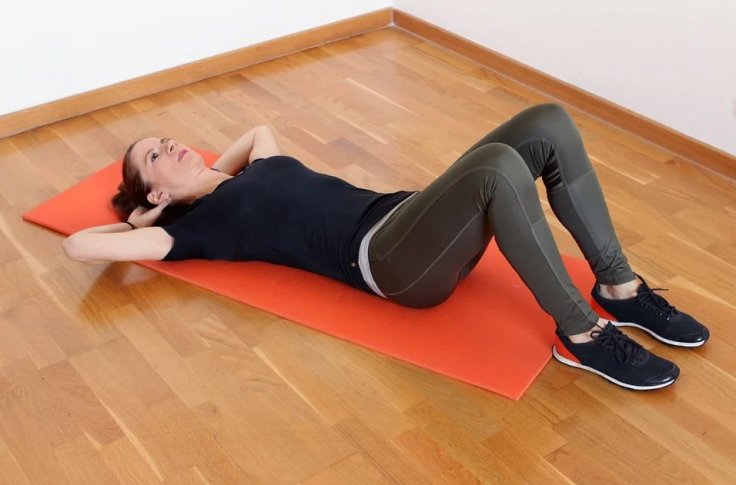

Incorporation of stress-reducing activities such as regular exercise, mediation, yoga, and other stress-relieving practices is a must, especially among older adults. Exercise must be structured over a long term as it can enable the enhancement of cardiovascular health among people of all fitness levels. Along with decreased chances of infection, it also awakens hibernating immune cells across the body, that fortify the defensive capacity of the immune system.
Shunning alcohol, smoking, and drugs as a way to come to terms with fear and anxiety is important. They impair immune functions on a cellular level by reducing the ability of organs and parts of the body such as the earlier mentioned gut lining that enhances the body's defenses. Staying in touch with friends and engaging in indoor activities with family can help tackle stress as well. Also, at a time when COVID-19 dominates the news, it can be upsetting to be exposed to it regularly. Therefore, picking a particular time of the day to update yourself with reliable news is a good option.
Sleep like a baby
Sleep is nature's stress-relieving gift to man. When one sleeps, the entire body, specifically vital tasks such as brain functions, find time to slow down and recoup. It has also been proven that stress hormones such as cortisol are found in increased levels when there is a lack of sleep. This is because the hormone is secreted in excess to keep the body alert and awake. Unfortunately, this redirects the energy required by the immune system to function well.
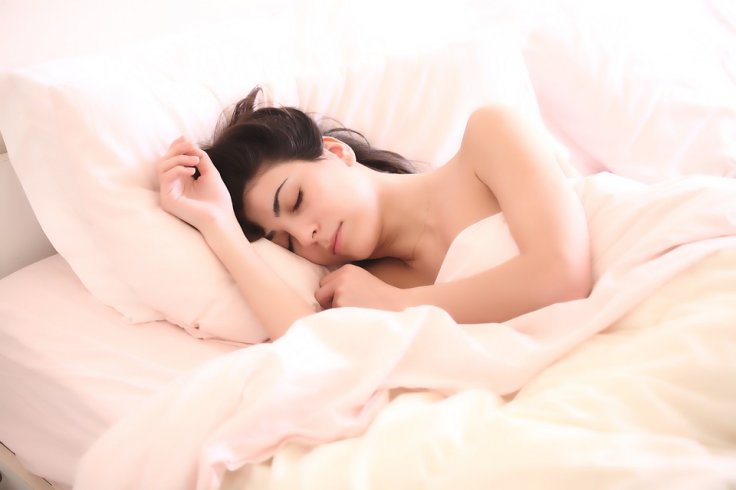

Research has shown among people who are suffering from severe sleep-deprivation, and those who sleep for less than six hours, T cell levels were found to be significantly lower, making them more prone to infections and cold. So putting your phones — that also have ill effects — away and providing your body the much-deserved rest it requires every night is a must. It not only improves immunity but also reduces stress and anxiety.
Fortify what is missing
Identifying the nutrients that are missing in your diet and supplementing it is important. For example, vitamin D is one such nutrient that several people are found deficient of. And among people who live in areas where there is limited exposure to sunlight, the levels of the vitamin can be very low. Therefore, supplementing it under medical supervision is a good way to go about it. Also, since it is a fat-soluble vitamin, it is must be consumed along with fatty for optimum absorption.

Inclusion of herbs such as turmeric, garlic, rosemary, oregano, and ginger is an excellent way of introducing anti-inflammatory compounds naturally within the diet. They also aid in fighting off viruses that cause respiratory problems.