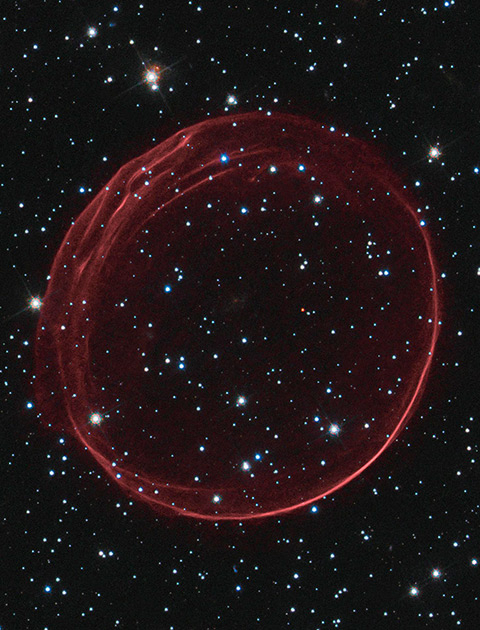
The US space organisation NASA shared a stunning photo of a supernova remnant located in a galaxy near Milky Way. Unlike other supernova events, the large cosmic object may have been caused by the violent collision between two stars.
The supernova remnant featured in NASA's photo has been identified as SNR 0509-67.5. It lies within the Large Magellanic Cloud, which is the small neighbouring galaxy of Milky Way. As per NASA, the supernova remnant is located about 160,000 light-years from Earth.
Collision Of Two Stars

SNR 0509-67.5 is classified as a Type 1a supernova, which indicates that it was created by a binary system of two stars orbiting one another. NASA noted that one of these stars, which is a white dwarf, may have self-destructed after absorbing the cosmic materials of its companion star. Another theory suggests that as these two stars orbited one another, they eventually collided and caused a massive explosion which resulted in a supernova.
"One explanation is that a white dwarf self-destructs after using its gravity to steal material from a nearby star, causing it to become unstable under the extra bulk and explode," NASA explained. "Another idea is that the detonation happens when two white dwarfs collide, destroying both objects."
The Supernova Remnant's Expansion
Although NASA stated that the explosion or collision took place about 400 years ago, the supernova remnant is still growing. According to the agency, the cosmic object's expansion is characterized by the crimson-coloured sphere. The expansion of this sphere is being pushed by the blast wave generated by the initial explosion.
Currently, SNR 0509-67.5 is about 23 light-years wide. Its expansion is moving at a rate of more than 11 million miles per hour. Near the upper-left portion of the supernova remnant are ripples in the expanding gas sphere. NASA explained that these ripples were caused by the ejection of uneven cosmic debris following the supernova event.