Finding fossils and making it as a new research project, is not the one and only priority or the job of a researcher, as there are certain mysteries that trigger adrenalin rush as well as the curiosity to know the million-year-old history. Some scientists also experienced a similar kind of situation after finding one group of organisms, which started to live on earth's surface nearly 500-million years ago.
In a science fiction film called "Life," audience have seen that how inside a spaceship's laboratory, a dead extraterrestrial organism, recovered from Mars, came back to life but unfortunately killed almost all the space crew members and used its intelligence to land on earth.
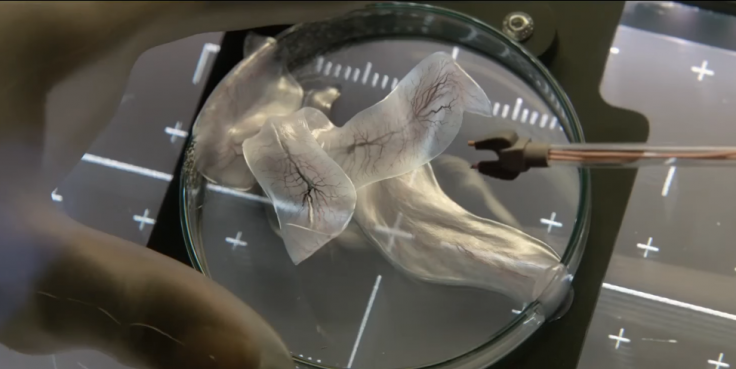
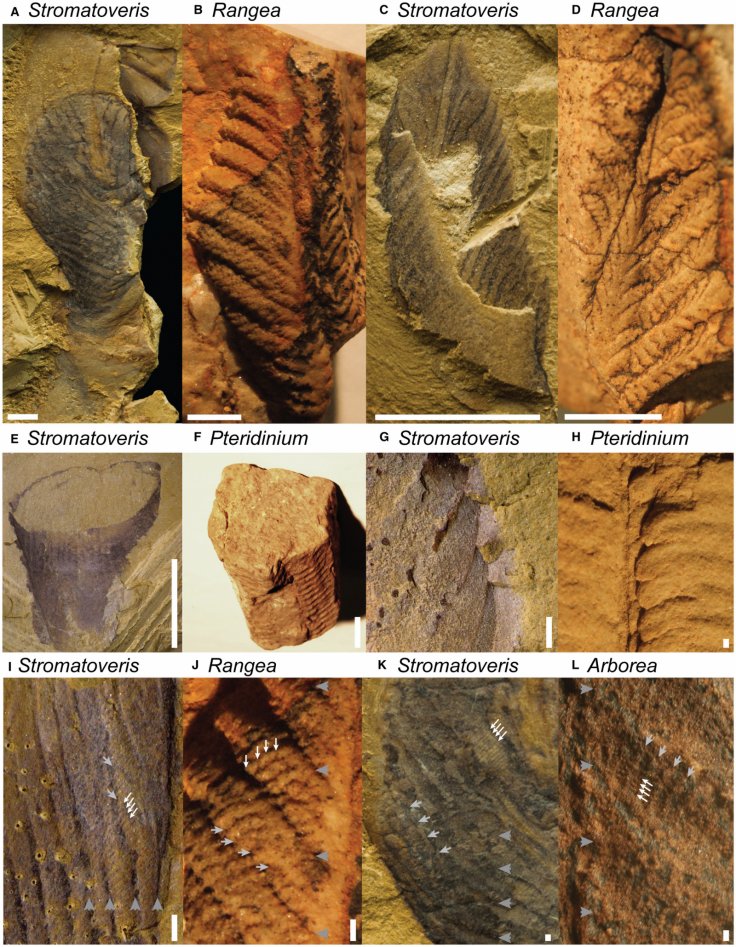
In reality, as per the scientists, the million-year-old group of organisms, which got its start in the Ediacaran period, looked like oversized leaves, exactly the way in the movie the alien creature was visualised. The scientists said that these organisms could measure up to two meters in length.
For several years scientists had no clue about the classification of this mysterious organisms. It made the scientists completely confused while they were trying to figure out whether it is a plant or animal or something in between. But, recently the new study, which was published in Palaeontology, stated that it is nothing but a type of animal, albeit ones that appear like an absolute alien here on Earth.
This research, which was conducted by multiple universities around the world, actually focused on the study of the fossils of a species called Stromatoveris psygmoglena. In the study, the researchers clearly stated that this previously unknown creature looked like large, ribbed leaves on the ancient ocean floor. But, further examination revealed that they were extremely weird animals, after comparing it with almost 200 known examples of the creature.
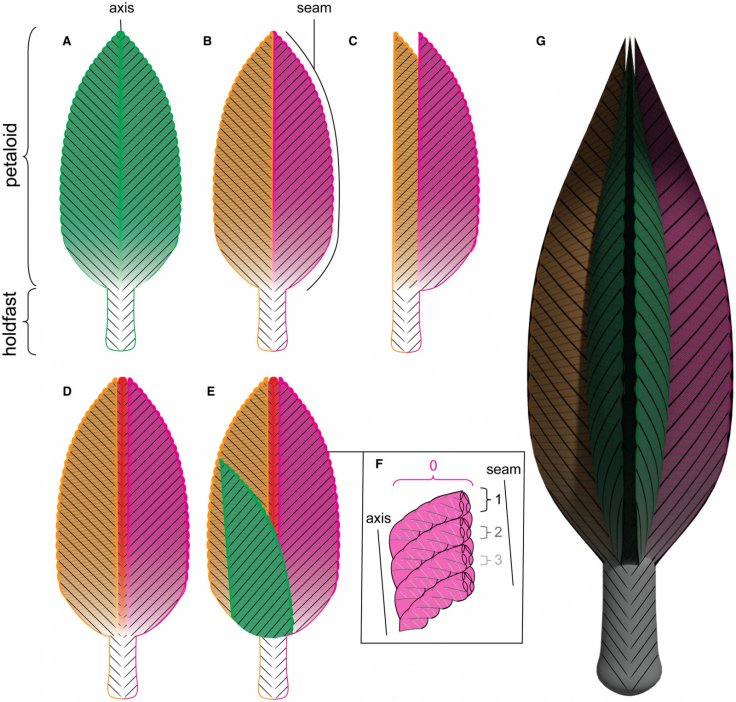
Finally a computer generated model helped the scientists to make an educated guess about its evolution. Now, the researchers believe that these organisms may have been an entirely new phylum of the animal kingdom. By using the data, scientists also claimed that it is a more complex creature than the sea sponges but they are also not very advanced like animals with full digestive systems.
Jennifer Hoyal Cuthill, a paleobiologist from the University of Cambridge and the Tokyo Institute of Technology, told Newsweek, The Ediacaran biota includes fossils of some of the oldest large and complex lifeforms known. These early fossils are not quite like anything alive today. So there has been a considerable scientific debate on where they belong in the tree of life."
"While it had been suggested that at least some of the large, complex fossils might have been early animals, almost every other possibility has also had its advocates: from seaweeds to giant protozoans," she added.
The study also revealed that since this creatures do not appear to have evolved into any other known organisms, this group of animals ran into a brick wall after thriving for tens of millions of years. However, still more research is required to establish any fact behind their extinction, but as per the scientists, that process could be almost impossible.