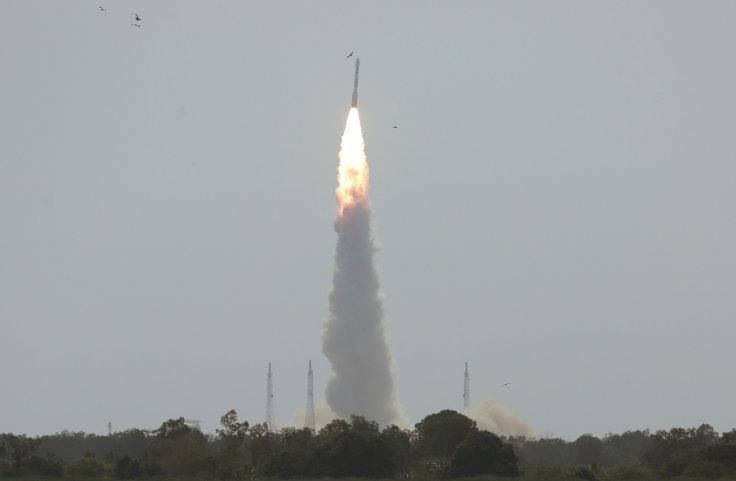
India plans to launch its sixth satellite of the Cartosat 2 series in its launch vehicle PSLV from Satish Dhawan Space Center (SHAR), in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh on January 10, 2018. The Cartosat would be launched along with 30 other foreign satellites.
The indigenous Cartosat satellites have various cartographic, urban and rural applications. They are used to monitor coastal land use, and regulation and utility management. Other Cartosat functions like monitoring of road networks, water distribution, and creation of land use maps, identification of geographical and man-made features are also analyzed using the satellites.
The Cartosats high-resolution images provide data's for the Land Information System (LIS) as well as for Geographical Information System (GIS) applications. The six Cartosat satellites have undergone series of technological upgradations since its initial launch in April 2008.
The Cartosat satellites also perform strategic civil and military roles which have been categorized as their key functions.
CARTOSAT-2A
Cartosat-2A, the 13th satellite in the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite series (IRS), had been launched on the PSLV-C9 rocket from SHAR on April 28, 2008. The 690-kg satellite was a sophisticated remote sensing satellite which provided scene-specific spot images by capturing high-resolution images by zooming into different regions of the country. The Panchromatic Camera (PAN) used in the satellite could capture quality black and white images of a region when focused till spatial resolution of 9.6 km per meter.
The satellite follows a polar Sun Synchronous Orbit (SSO) which passes through same locations during specific local timings making it an apt tool for ground observations.
CARTOSAT-2B
Cartosat-2B, the second satellite of the Cartosat 2 series was launched as the 17th satellite in the Indian Remote Sensing Satellite series (IRS), from the SHAR using the PSLV-C15 rocket on July 12, 2010. The PAN camera used in the satellite was able to capture quality images from a geographic strip of 9.6 km with 1 spatial resolution of 1 meter.
This 694 Kg weighing cartosat satellite can be steered up to 26 degrees along its orbit to obtain 3-dimensional stereoscopic imagery. This satellite also follows orbitals similar to Cartosat 2A.
CARTOSAT-2C
The Cartosat-2C satellite was launched from the SHAR on June 22, 2016, using a PSLV-C34 rocket. This satellite uses Panchromatic and Multi-spectral cameras for more precise studies including the creation of land use maps and detection of geographical and manmade features apart from features of its predecessors. The satellite had a mass of 737.5 kg during its launch.
The ground images provided by Cartosat-2C had been used by the Indian Army during their surgical strike on Pakistan in September 2016.
CARTOSAT-2D
The fourth satellite of the Cartosat-2 satellite series, Cartosat-2D, had been a part of PSLV's historical launch of 104 satellites on February 15, 2017. Two Indian nanosatellites along with 101 nanosatellites from United States of America, Kazakisthan, Isreal, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the United Arab Emirates were successfully launched along with the 712 Kg Cartosat-2 satellite during this historic mission.
CARTOSAT-2E
Cartosat-2E which had been launched on June 23, 2017, along with 29 other satellites in PSLV launcher from the SHAR has significant civil and military functions as it could accurately spot objects within a square of 0.6 meters by 0.6-meter radius. The 243-kg satellite was placed in a SSO orbit at 505 Km height.